如何创建自己的form表单组件?
- 发现一个还不错的文章 文章链接
所需知识:
- 实现自己的v-model
- 利用slot插槽,写出el-form-item
- 使用prop传参定义校验字段,emit抛出数据
GitHub上一个比较有名的项目,里面有些功能实现值得学习。
整个实现(mock-js,dev-server,chokidar)还需要node\express相关知识,总体实现就是使用 dev-server,将mock出的数据返回。
1 | module.exports = { |
1 | app.use(bodyParser.json()) |
1 | function registerRoutes(app) { |
昨天打码的时候,发现使用
1
require('@/mock/index')
vscode没有对这个路径进行跳转,第一时间,我想的是,@别名导致的,但是其实我本人有写jsconfig.json,但是谷歌搜索都是这样.我便开始一段对该配置文件探索和迷惑的一段时间…
其实,自带就有跳转,主要是因为,我在index.js里没有写
1 | module.exports={} |
好了,误会解除…
这些路径啊智能跳转啥的,本质就是读取目录以及内容,用的node fs模块来完成..估计就是检测不到导出,就不会有跳转了..
1 | Usage: webpack serve|server|s [entries...] [options] |
1 | // resolve用来拼接绝对路径的方法 |
1 | const { resolve } = require('path') |
今天面试被问到一个问题,之前都没遇见过,问父子组件生命周期加载顺序,把我整懵了.
1.加载渲染过程
父beforeCreate->父created->父beforeMount->子beforeCreate->子created->子beforeMount- >子mounted->父mounted
2.子组件更新过程
父beforeUpdate->子beforeUpdate->子updated->父updated
3.父组件更新过程
父beforeUpdate->父updated
4.销毁过程
父beforeDestroy->子beforeDestroy->子destroyed->父destroyed
组件的调用顺序都是先父后子,渲染完成的顺序肯定是先子后父
组件的销毁操作是先父后子,销毁完成的顺序是先子后父
当dom渲染时,会createElm创建元素,创建元素后会进行初始化,初始化组件的时候内部还有组件,会不停的去渲染,所以它的渲染顺序是先父后子,完成的顺序是先子后父。
dom渲染描述:先父组件要创建beforeCreate、created,父组件实例化完成后要挂载这个父组件beforeMount,挂载父组件的时候会调用父的render方法,渲染的时候发现里面有子组件,这时就会调用子组件的beforeCreate、created、beforeMount,当子组件都完成之后,会把子组件先存起来,这儿有队列,不是子完成就会调用子的mounted,因为子组件中可能还有子组件,这时会暂存一下,到最后子全完成了会按照子调父的调,mounted是先子后父。
源码:在dom渲染和更新时就会调用patch方法,在patch方法中有一个insertedVnodeQueue数组,会将所有的vnode存放在insertedVnodeQueue中,最后会在整个创建完之后会调用invokeInsertHook方法,依次调用收集的insert hook。在patch中会调用createElm方法来创建元素,createElm方法中会对元素进行判断:如果元素是组件,会调用createComponent方法创建组件,调用组件的init方法渲染当前组件的内容,通过initComponent方法将pendingInsert插入到自己的insertedVnodeQueue中,然后将它置为null,最后会调用invokeCreateHooks方法将vnode存放在insertedVnodeQueue中;如果元素不是组件,会调用createChildren方法递归遍历子节点(子组件),createChildren方法中会再次调用createElm方法,直到元素不是一个组件时。
当所有组件都完成后,会调用invokeInsertHook方法,里面会循环通过insert方法依次调用收集的hook,在insert方法中就会触发mounted。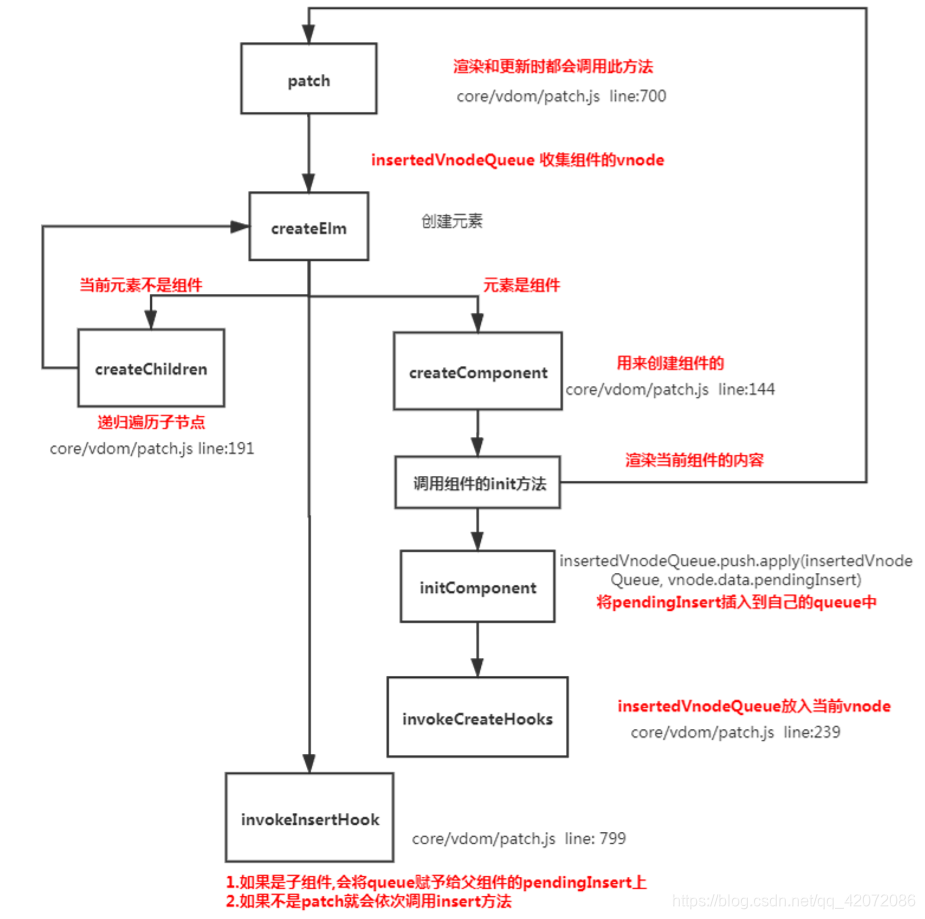
现在想象,我们正在 debug 一个 app 并且观察 devtool 中的 mutation 日志。每一条 mutation 被记录,devtools 都需要捕捉到前一状态和后一状态的快照。然而,在上面的例子中 mutation 中的异步函数中的回调让这不可能完成:因为当 mutation 触发的时候,回调函数还没有被调用,devtools 不知道什么时候回调函数实际上被调用——实质上任何在回调函数中进行的状态的改变都是不可追踪的。
今天被问得有点奇怪,说为什么有了action还要mutation…事实上action只是当一个延后提交mutation的方法,真正改数据的还是mutation.也就不存在,两者重复一说.
许多开发人员经常混淆作用域和执行上下文的概念,误认为它们是相同的概念,但事实并非如此。
我们知道 JavaScript 属于解释型语言,JavaScript 的执行分为:解释和执行两个阶段,这两个阶段所做的事并不一样:
1.词法分析
2.语法分析
3.作用域规则确定
1.创建执行上下文
2.执行函数代码
3.垃圾回收
1.JavaScript 解释阶段便会确定作用域规则,因此作用域在函数定义时就已经确定了,而不是在函数调用时确定,但是执行上下文是函数执行之前创建的。执行上下文最明显的就是 this 的指向是执行时确定的。而作用域访问的变量是编写代码的结构确定的。
2.作用域和执行上下文之间最大的区别是:
执行上下文在运行时确定,随时可能改变;作用域在定义时就确定,并且不会改变。
3.一个作用域下可能包含若干个上下文环境。有可能从来没有过上下文环境(函数从来就没有被调用过);有可能有过,现在函数被调用完毕后,上下文环境被销毁了;有可能同时存在一个或多个(闭包)。同一个作用域下,不同的调用会产生不同的执行上下文环境,继而产生不同的变量的值。
Vite到手,先新建了个Vue3项目,之前基本看了文档以及一些新语法,第一次用起来有几个看法:
1.新建的Vue模板文件中,有实验性因素,Vetur甚至没法识别script setup语法糖。
2.defineProps方法甚至在官网没出现相关介绍,虽然就是一个为props添加属性限定,同时return出去。
3.代码上,更方便也更加清晰一点,聚合API也不会像之前那样十几个方法写一页,在接触Vue2项目的时候这个确实是最烦的。
感觉还是得等有些语法成为正式版先.. 不然这语法提醒顶不住。
1 | Markdown 目录: |
学习Vue3时期,顺带被尤小右安利一波Vite。看过文档,大概理解是一个打包构建工具,但不同于webpack,他采用ESbuild,也即是使用浏览器支持的<script type="module" /> 来引入依赖的文件。Vite担当服务器的作用,利用缓存,以及其他机制来达到甩开webpack的速度。
留个官网中文文档地址:为什么选Vite | Vite 官方中文文档 (vitejs.dev)